![[Experimental]](figures/lifecycle-experimental.svg)
Functions that use the Bland-Altman method to assess the agreement between two numerical vectors.
Usage
s_bland_altman(x, y, conf_level = 0.95)
g_bland_altman(x, y, conf_level = 0.95)
Arguments
- x
(numeric)
vector of numbers we want to analyze.
- y
(numeric)
vector of numbers we want to analyze, to be compared with x.
- conf_level
(proportion)
confidence level of the interval.
Value
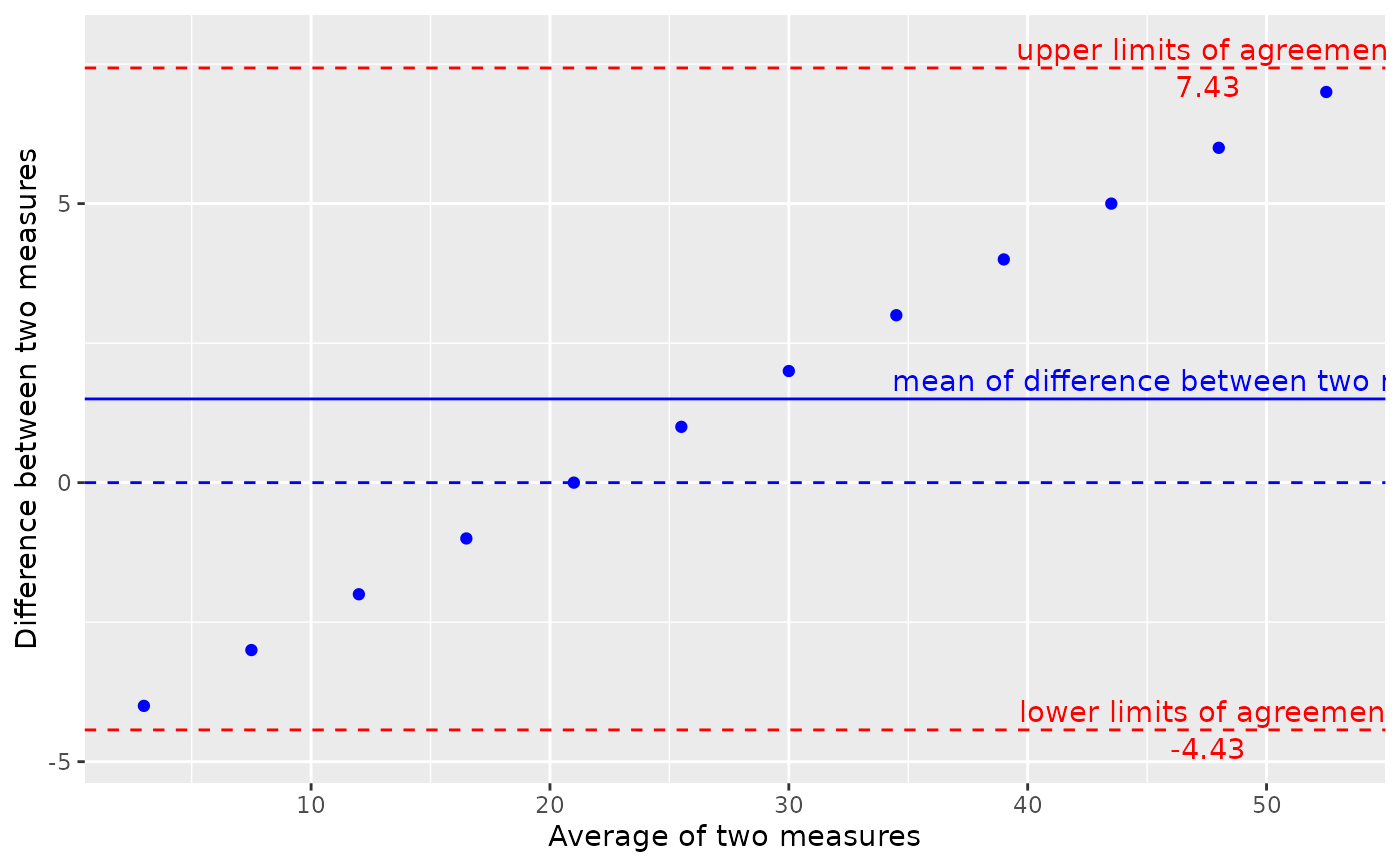
s_bland_altman() returns a named list of the following elements: df, difference_mean, ci_mean,
difference_sd, difference_se, upper_agreement_limit, lower_agreement_limit, agreement_limit_se,
upper_agreement_limit_ci, lower_agreement_limit_ci, t_value, and n.
Functions
s_bland_altman(): Statistics function that compares two numeric vectors using the Bland-Altman method
and calculates a variety of statistics.
g_bland_altman(): Graphing function that produces a Bland-Altman plot.
Examples
x <- seq(1, 60, 5)
y <- seq(5, 50, 4)
conf_level <- 0.9
# Derive statistics that are needed for Bland-Altman plot
s_bland_altman(x, y, conf_level = conf_level)
#> $df
#> average difference
#> 1 3.0 -4
#> 2 7.5 -3
#> 3 12.0 -2
#> 4 16.5 -1
#> 5 21.0 0
#> 6 25.5 1
#> 7 30.0 2
#> 8 34.5 3
#> 9 39.0 4
#> 10 43.5 5
#> 11 48.0 6
#> 12 52.5 7
#>
#> $difference_mean
#> [1] 1.5
#>
#> $ci_mean
#> [1] -0.3692162 3.3692162
#>
#> $difference_sd
#> [1] 3.605551
#>
#> $difference_se
#> [1] 1.040833
#>
#> $upper_agreement_limit
#> [1] 7.430604
#>
#> $lower_agreement_limit
#> [1] -4.430604
#>
#> $agreement_limit_se
#> [1] 1.802776
#>
#> $upper_agreement_limit_ci
#> [1] 4.193027 10.668181
#>
#> $lower_agreement_limit_ci
#> [1] -7.668181 -1.193027
#>
#> $t_value
#> [1] 1.795885
#>
#> $n
#> [1] 12
#>
# Create a Bland-Altman plot
g_bland_altman(x = x, y = y, conf_level = conf_level)